Simulation of cable and wire heating by electromagnetic induction
Induction heating is transforming the cable and wire industry by providing a reliable, energy-efficient, and non-contact heating method for ferrous and non-ferrous materials. From drying and curing coatings to preheating for extrusion and heat treatment processes like annealing and hardening, induction ensures precise temperature control without the drawbacks of flame-based heating. However, achieving uniform heating in multi-strand cables presents unique challenges due to electromagnetic proximity effects and shielding between wires.
That’s where simulation comes in. Using CENOS Induction Heating simulation software, engineers can optimize heating parameters, ensuring surface-to-core temperature uniformity even in complex multi-wire setups. This article explores a real-world simulation of a 3 cm stranded wire heated to 850°C, showcasing how simulation helps reduce physical testing, cut development time, and create precise heating recipes.

Typical applications include:
- Drying post-cleaning or removing water or solvent from coatings
- Curing of liquid or powder-based coatings. Providing a superior bond strength and surface finish
- Diffusion of metallic coating
- Pre-heating for extrusion of polymer and metallic coatings
- Heat treatment including stress relieving, tempering, annealing, bright annealing, hardening, patenting etc.
- Pre-heating for hot-forming or forging, especially important for specification alloys
Induction is also used for the preheating, post-heating, or annealing of metallic wire along with the bonding/vulcanization of insulating or shielding within various cable products. Preheating applications can include heating wire prior to drawing it down or extruding. Post-heating would typically include processes such a bonding, vulcanizing, curing or drying paint, adhesives, or insulating materials.
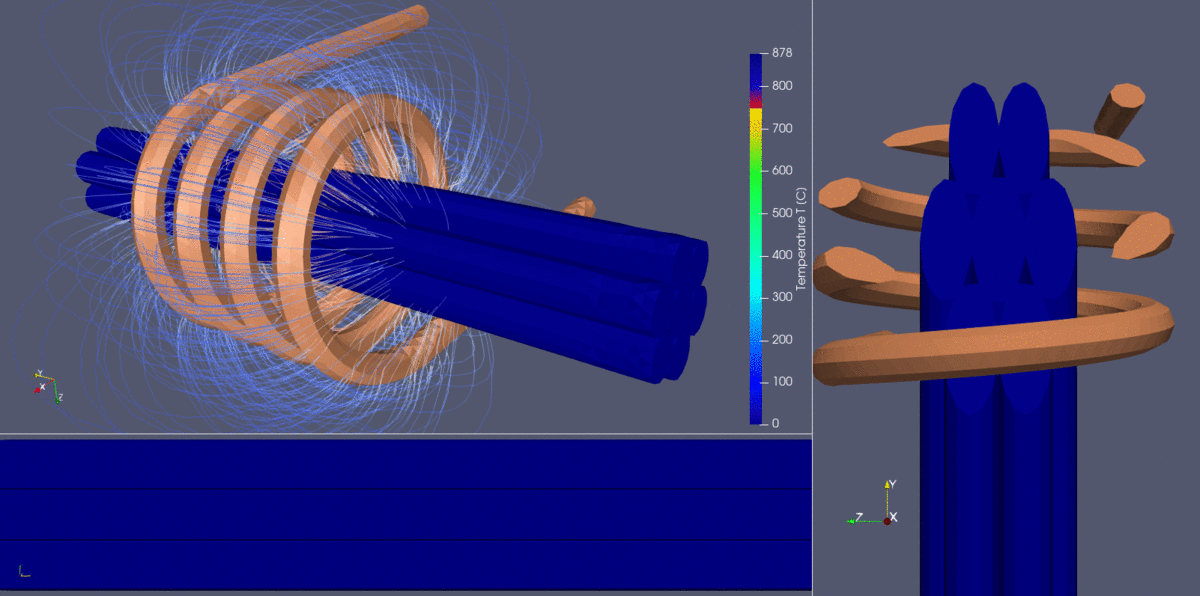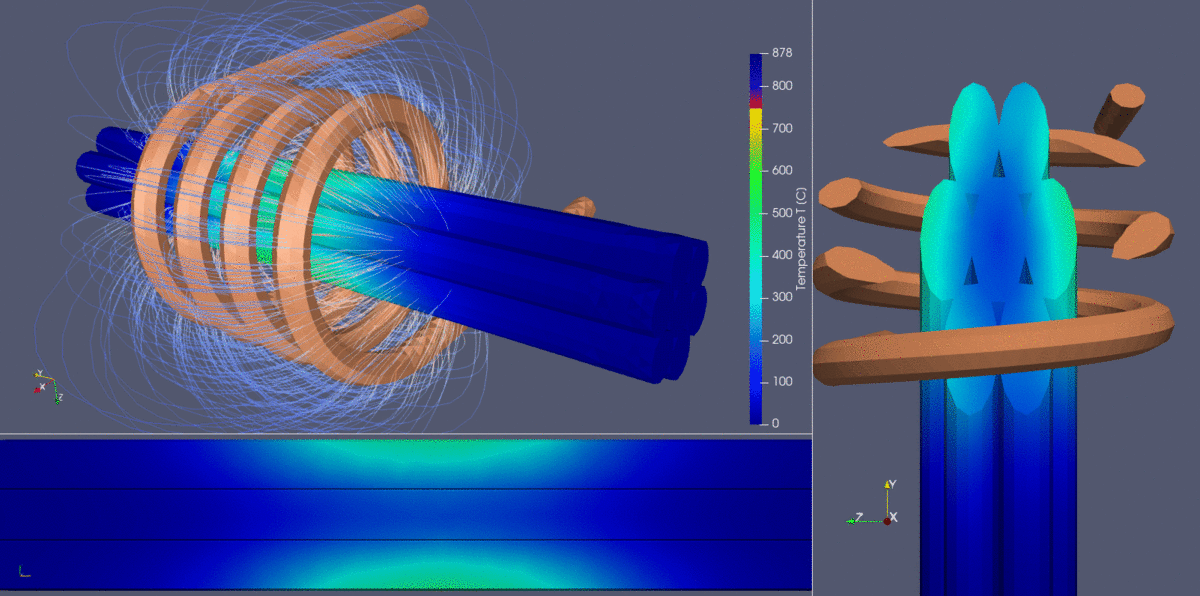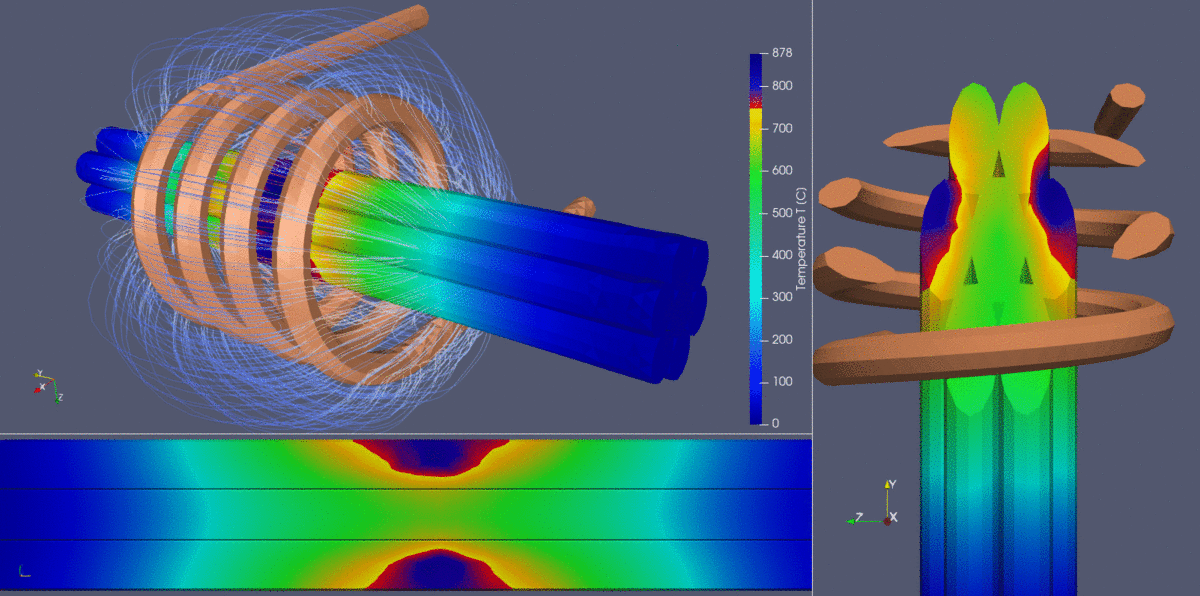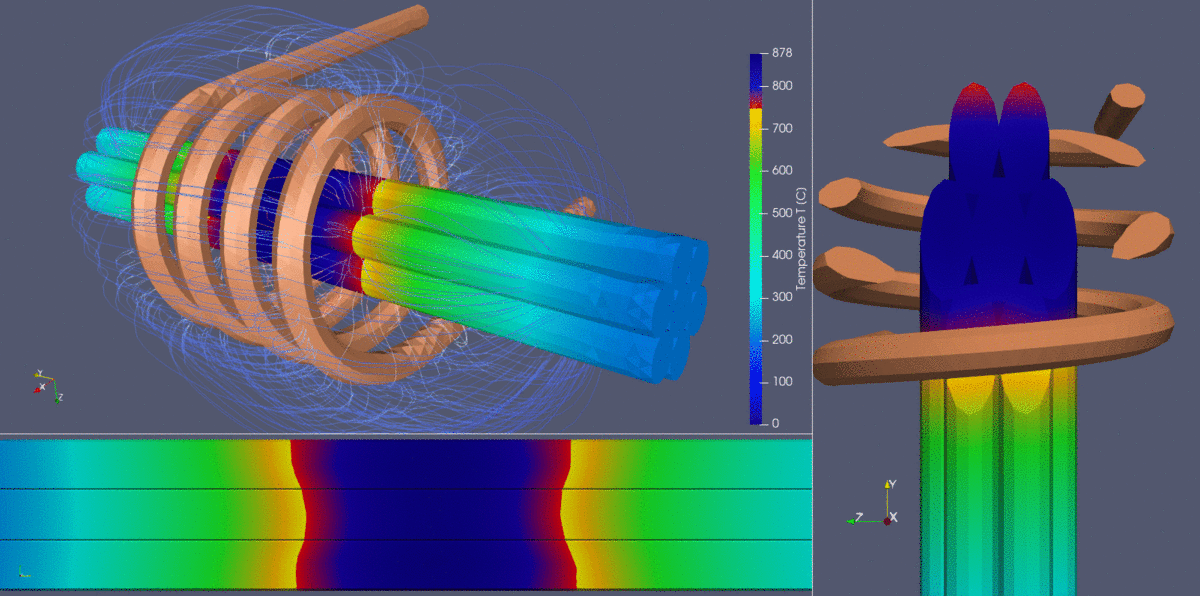
Here’s a stranded wire (diameter – 3 cm) heating simulated with CENOS Induction Heating simulation software, the objective of the simulation was to achieve surface-to-core temperature uniformity. In most single-wire processing applications with wire diameters less than 3 mm, the entire wire is usually heated through and the criterion of obtaining surface-to-core temperature uniformity is not an issue unless extremely short heat times are used.
Therefore, when heating multiple wires running in parallel or multi-strand cables, the criterion of providing an equal temperature in all wires regardless of their position inside the inductor becomes critical. The former is a result of the fact that external and internal wires of the cable may be heated differently because of the electromagnetic proximity effect and electromagnetic shielding of the external vs. internal wires.
- Frequency: 5 kHz
- Heating time: 15 sec.
- Current: 1000A
- Max. heating temperature: 850 degrees Celsius
- Material: Medium or Low carbon steel
- Coil type: multi-turn solenoid inductors are commonly used for heating single wires or multi-strand cables.
This simulation animation shows the electromagnetic induction heating of a stranded wire bundle using a multi-turn solenoid inductor. The visualization provides a detailed look at the heating dynamics, highlighting how electromagnetic fields interact with the wire strands and how temperature is distributed throughout the process.
Key observations
- Electromagnetic field lines:
- The blue lines around the coil represent the electromagnetic field generated by the alternating current flowing through the solenoid inductor.
- These fields induce eddy currents in the stranded wires, generating resistive heating in the metal conductors.
- Temperature distribution & heat uniformity:
- The color gradient in the wire bundle indicates temperature variation, ranging from cooler blue tones (~100°C) to hotter yellow-orange tones (850°C+).
- The challenge in heating multi-strand cables is ensuring uniform temperature across all wires. The external wires are exposed to stronger electromagnetic fields, leading to potential overheating, while internal wires may experience shielding effects, reducing heating efficiency.
- Achieving a balance where the core and surface wires reach uniform heating levels is crucial for process optimization.
- Heating parameters in action:
- Frequency: 5 kHz – ensuring deep penetration heating suited for medium-carbon steel.
- Heating time: 15 seconds – a short but effective duration to reach the desired 850°C target.
- Current: 1000 A – a substantial energy input driving the induction process.
- Inductor type: Multi-turn solenoid, a commonly used configuration for cylindrical heating applications like wires and cables.
- Electromagnetic proximity & shielding effects:
- Due to electromagnetic proximity effects, the outer wires experience higher heating rates, while the inner wires tend to heat more slowly due to shielding.
- The simulation clearly illustrates these effects, helping engineers adjust process parameters such as coil positioning, frequency, and heating time to optimize uniformity.
Why this matters for engineers
This type of simulation is critical in the cable and wire industry, where achieving consistent and repeatable heating is essential for processes like preheating before extrusion, stress relieving, annealing, and coating applications. By using CENOS Induction Heating simulation software, engineers can fine-tune their induction heating setup, reducing costly physical prototyping and accelerating production efficiency.
This simulation is a perfect example of how smart engineering meets practical application—helping manufacturers create optimized heating “recipes” with confidence.
Reduce the number of physical tests and development time of induction coil and systems. Create heating recipes with confidence with CENOS. Start your free trial today!


