Pipe rolling pre-heating for welding
In modern welding processes, preheating the material is a critical step that ensures better joint quality and prevents issues like cracking or brittle welds. One method engineers use to achieve this is induction heating, where electromagnetic fields heat the material. In this article, we will explore the simulation of an induction heating system preheating a large pipe, focusing on how this rolling inductor works and what this specific simulation shows.
Understanding the simulation
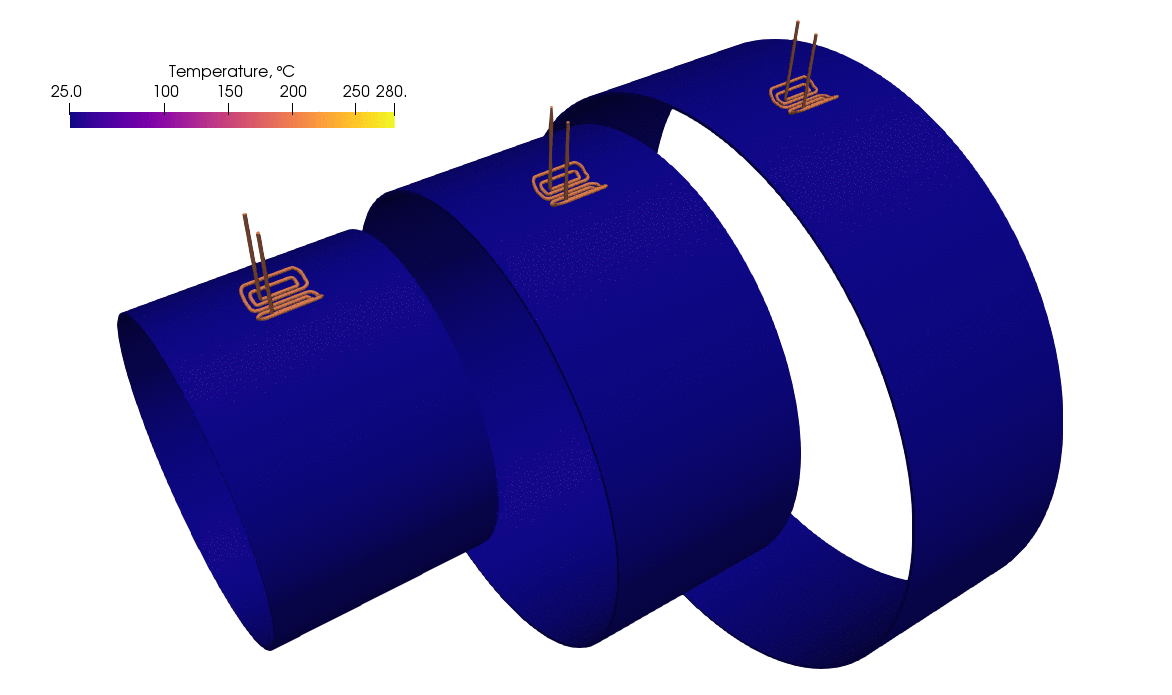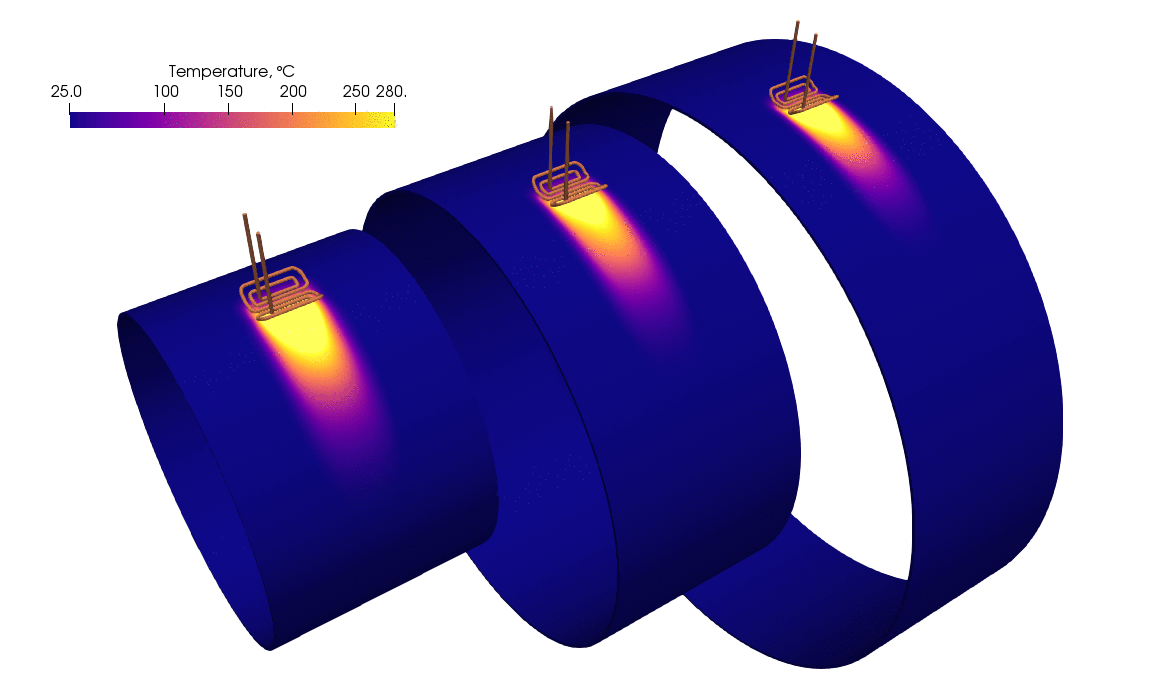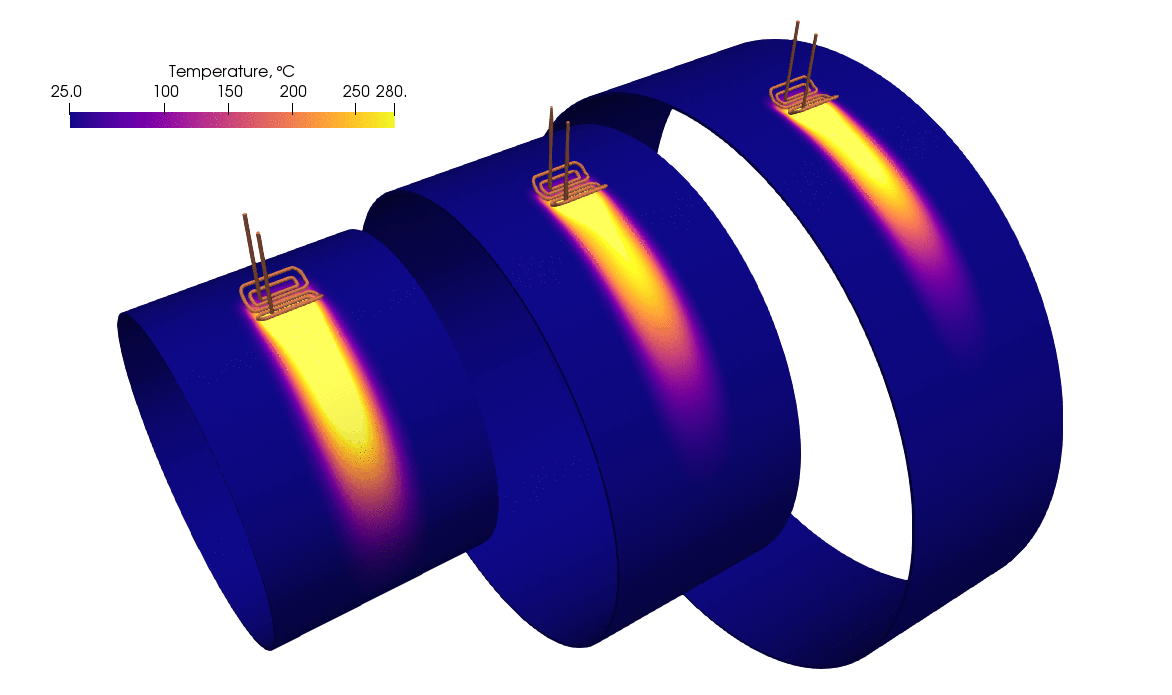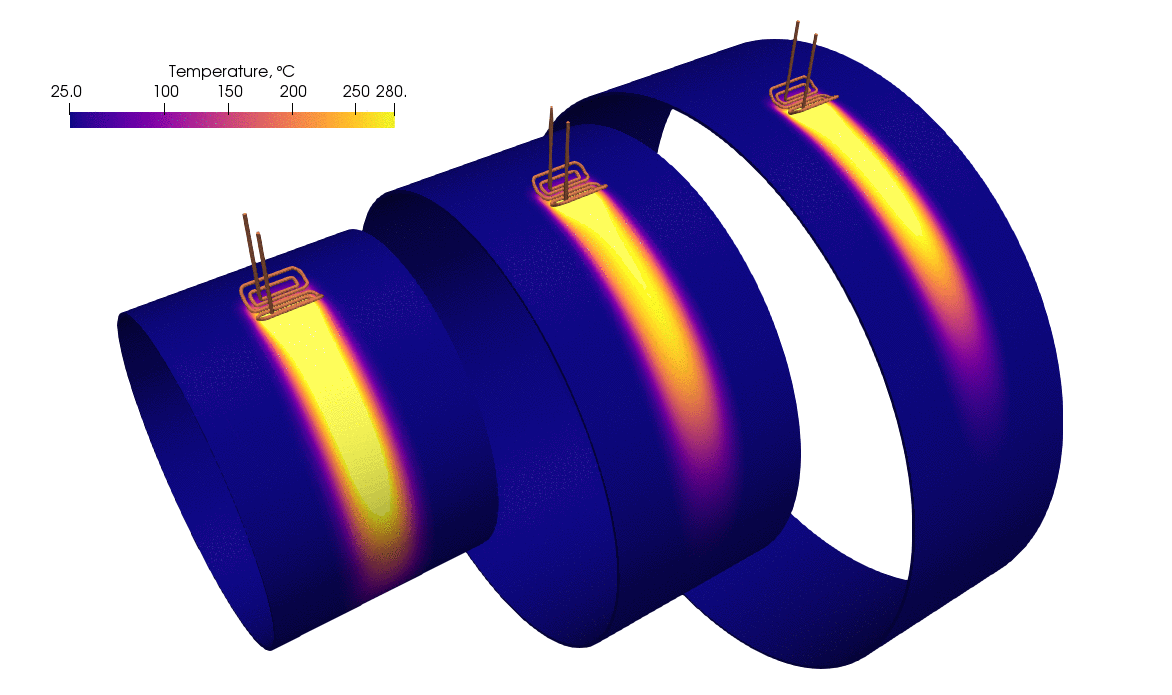
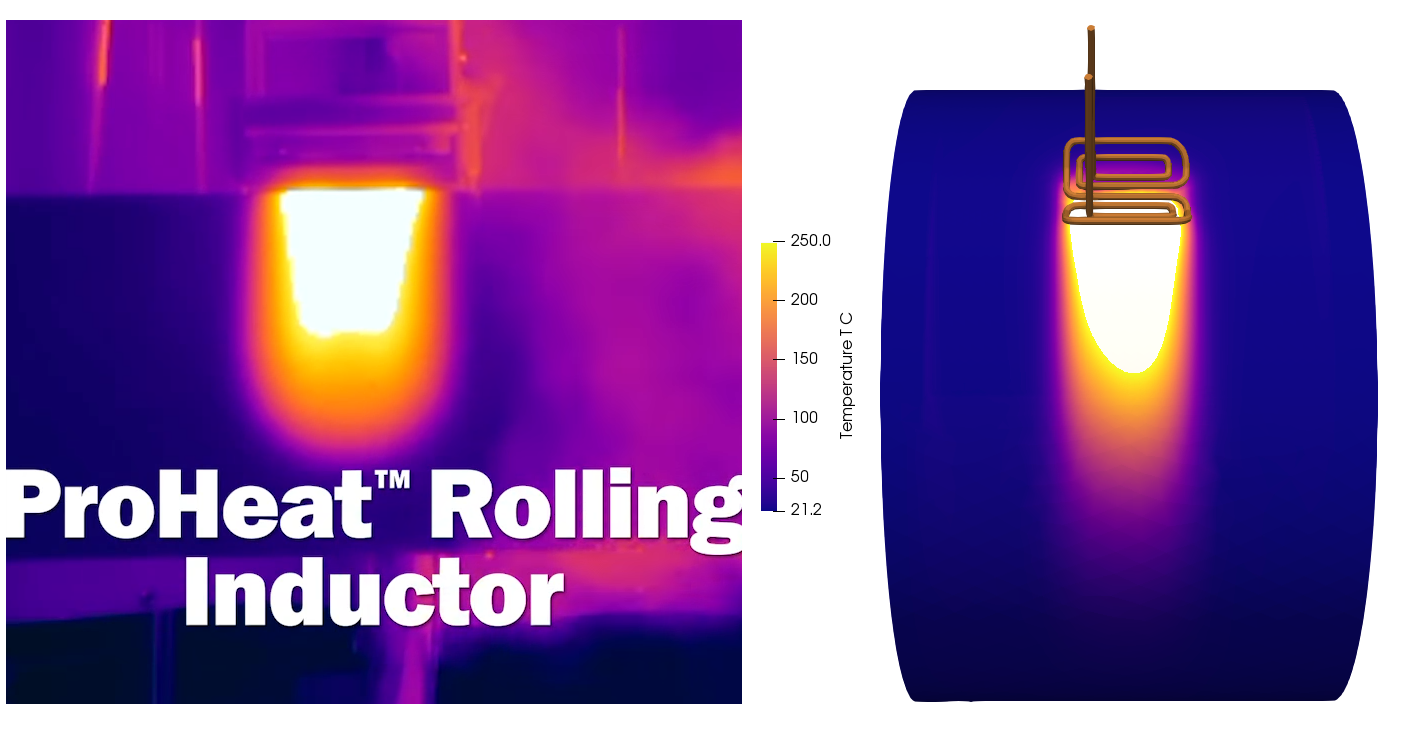
The image depicts a simulation of a rolling inductor used to preheat a large cylindrical pipe before welding. As shown in the simulation, the pipe undergoes progressive heating as the rolling inductor moves along the pipe’s surface.
Key highlights from the simulation:
- Induction heating coils: The orange-colored coils represent the inductor coils responsible for generating an electromagnetic field. This field induces currents (eddy currents) in the metallic pipe, which leads to resistive heating.
- Heat distribution: The temperature scale on the top left indicates a range from 25°C to 280°C. Initially, the pipe is at a cooler temperature (blue zones), and as the rolling inductor passes, the heat generated causes the pipe to warm up to temperatures around 280°C, as evidenced by the yellow-to-red gradient in the simulation.
- Rolling motion: The coils are mounted on a structure that moves along the surface of the pipe. This motion ensures that the entire circumference of the pipe gets heated evenly, which is crucial for a consistent weld quality.
- Gradual temperature increase: The simulation illustrates that as the inductor passes over different sections of the pipe, the temperature rises in those areas. This progressive heating prevents sudden temperature jumps that could lead to thermal stress, ensuring a controlled and uniform preheating process.
The significance of preheating in welding
Preheating metal before welding has several important benefits:
- Reduces thermal stress: When a cold pipe is welded, the heat from the welding torch creates a temperature differential between the welded area and the rest of the material, leading to thermal stress. Preheating reduces this stress, minimizing the chances of cracks.
- Improves weld penetration: Heating the material before welding allows better penetration of the weld bead, ensuring a stronger joint.
- Minimizes hydrogen-induced cracking: Preheating helps to expel moisture from the material, reducing the hydrogen content, which is a common cause of cracking in welds.
Why induction heating is preferred
Induction heating is an efficient and precise method for preheating large structures like pipes. Compared to traditional heating methods (such as gas burners), induction offers:
- Localized heating: The ability to heat only the required portion of the material with minimal energy loss to the surroundings.
- Speed: Induction heating is faster than other methods because the electromagnetic field directly generates heat within the material.
- Controllability: Engineers can easily control the intensity of heating by adjusting the current and speed of the rolling inductor, ensuring uniform preheating throughout the pipe’s surface.
Analyzing the results
The simulation demonstrates an effective and even preheating of the pipe, which is vital for achieving optimal welding conditions. The temperature gradient reveals that the inductor can generate a controlled, smooth increase in temperature. This indicates that engineers using this method can achieve:
- Uniform temperature: There are no significant cold or overheated spots, which means the heat is distributed evenly across the pipe’s surface.
- Precise control: The movement of the rolling inductor allows precise control of where and how much heat is applied, ensuring the preheating process is accurate without wasting energy.
The rolling inductor preheating process provides engineers with a reliable and efficient way to prepare large pipes for welding, especially in industries like oil and gas where large pipelines are common.
Conclusion
Simulations like this one highlight the benefits of using induction heating for preheating pipes before welding. The controlled and even heat distribution seen in the simulation ensures that the pipe is properly prepared, reducing the risk of defects in the weld. For engineers who frequently work with large-scale welding operations, the use of induction heating provides an energy-efficient and highly effective solution, leading to better results and reduced post-weld complications.
As this simulation shows, leveraging modern software to visualize heat distribution and understand the preheating process helps engineers fine-tune their operations, optimizing both time and material quality.


