Hardware requirements for CENOS
When induction heating engineers decide to switch from manual calculations and physical testing of their designs to computer simulations, many things come in question when choosing the correct software. One of them is the requirements for the computer on which the simulations will be run, because what good is a software if you cannot use it on your computer?
In this article we will look into hardware requirements for CENOS Platform – simple 3D modelling and simulation software for induction heating.
How hardware affects calculation time?
The limitations for induction heating simulations are mainly connected with calculations of electromagnetic (EM) field, which is most efficiently solved using direct solver. The limitation factor for direct solver is the size of matrix to solve. In EM calculation unknown for electric field is located in mesh nodes, but unknown for magnetic field is located on edges of mesh elements, meaning that bigger mesh element count will increase the size of matrix to solve and prolong the calculation time.
As CENOS uses only one CPU at a time, RAM size has a greater role in calculation time. Larger RAM will enable the user to run simulations faster, as well as run simulations with larger mesh.
Mesh size starts to affect the calculation time when 3D simulations are run, as mesh element count for 2D geometries does not usually reach such high numbers. For 3D simulations the volume element count will be used as a criterion to determine the size of the mesh.
Hard drive affects the calculation time as well, although not as much as RAM size. If your simulation case folder is saved on SSD, the data writing in that folder while simulation is calculating will happen faster if compared to a case which is saved on HDD.
How to know the element count?
The determination of mesh volume element count is the first step into understanding if your machine will be enough for a specific case or will you need to upgrade it. There are two different ways on how to know the volume element count of your simulation.
Those who use Templates or From CAD geometry creation approaches and do not manually interact with mesh can find mesh statistics in CENOS Physics part under the geometry preview window. Number of elements will give you an understanding of the size of your case.
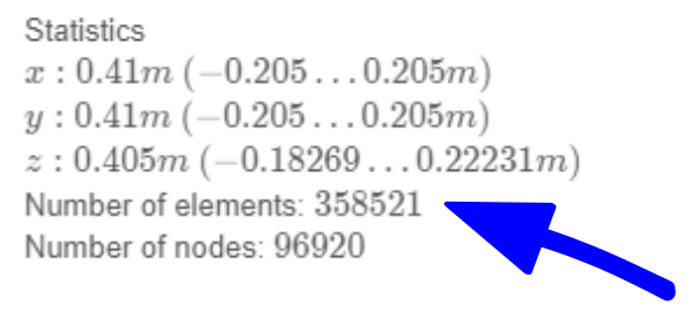
Note: the Number of elements in CENOS includes both volume and surface elements, which means that the real volume element count is a little lower than this.
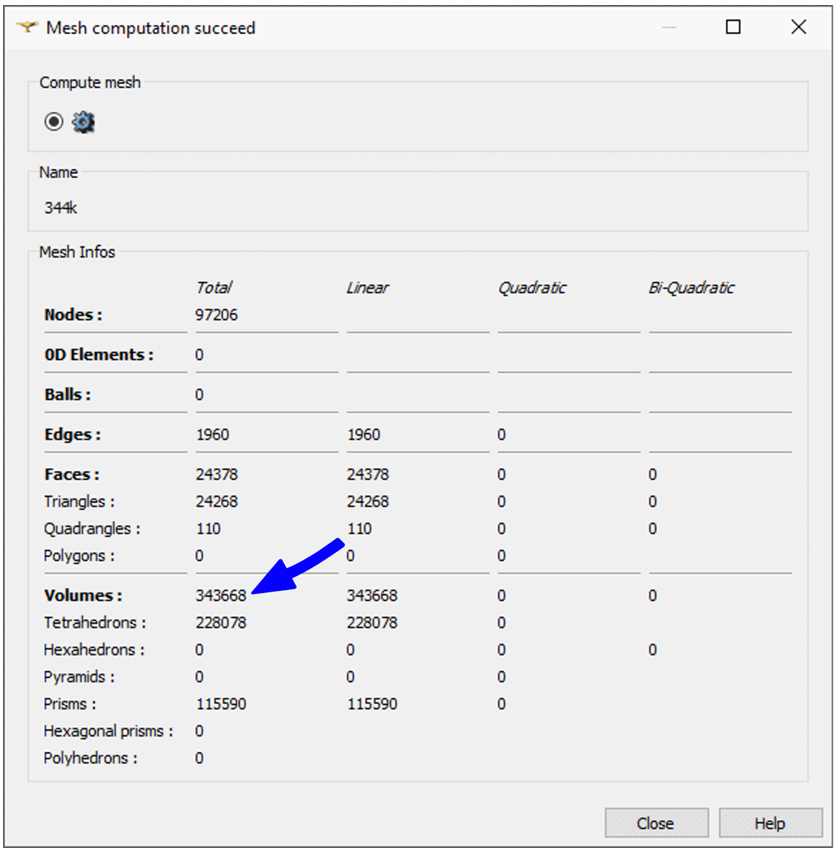
More advanced users who are building their case manually, can find the precise volume element count when calculating the mesh in Salome. After calculation a Mesh computation succeed window will open, where you can find the total volume element count.
Benchmark case
We created a benchmark test case to see how RAM size affects the calculation time of different meshes.

A simple spur gear and one-winding solid inductor at 8 kHz frequency and 10 kA current
The test case is harmonic electromagnetic analysis of a simple spur gear and two-winding solid inductor at 8 kHz frequency and 10 kA current. It does not show the exact time the user will require for the induction heating calculation, rather it shows the time required to do electromagnetic calculation, which is repeated many times during real case of induction heating.
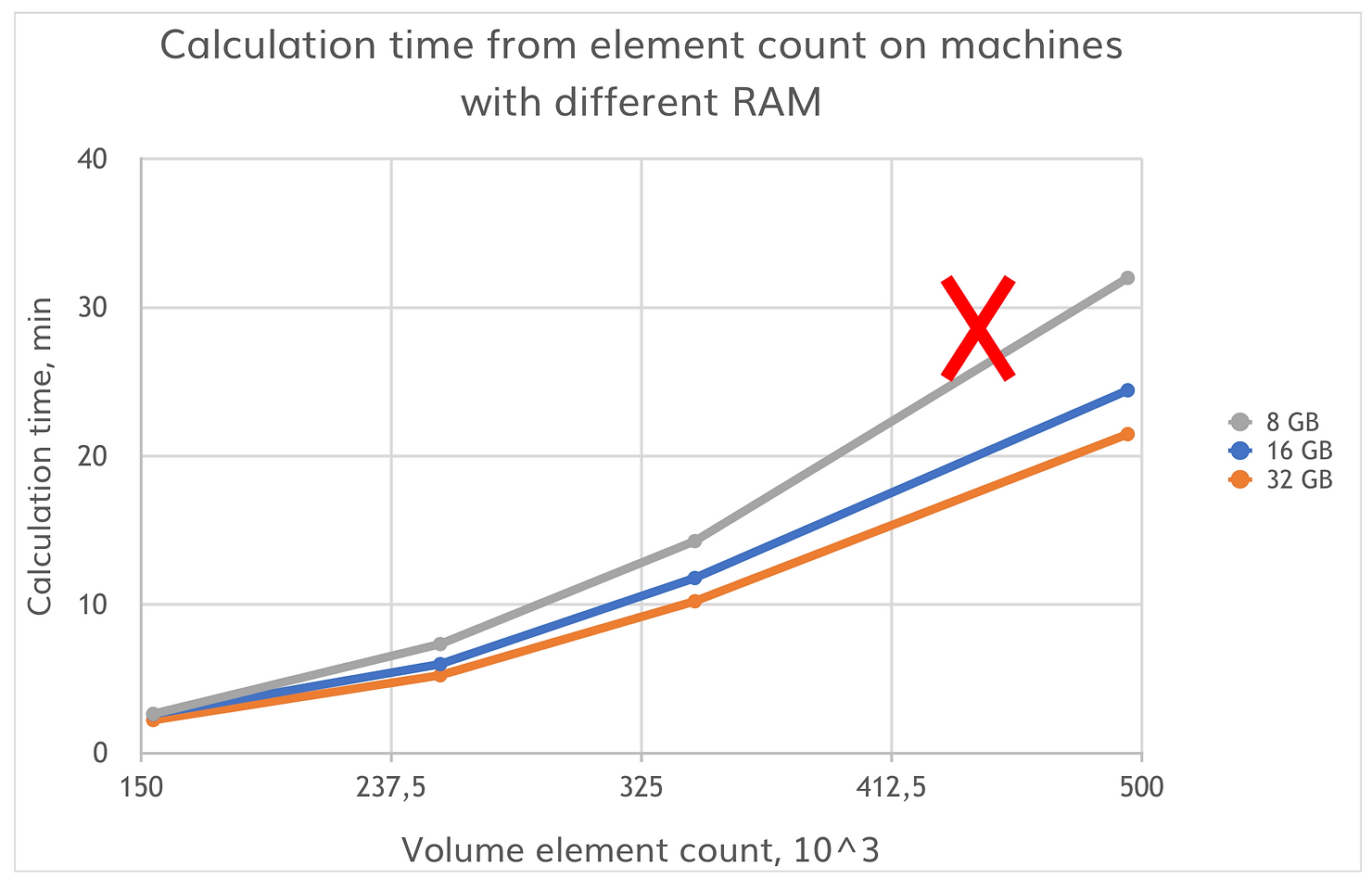
Test was carried out on 3 different machines (with 8, 16 and 32 GB RAM) with 4 different meshes of the same geometry (with element count of 154k, 254k, 344k and 495k).

At low element count (154k) the calculation time is almost the same for different RAM settings. We can start to see a difference in calculation time when element count is higher (254k – 344k), and at relatively large mesh size (495k) the machine with 8 GB RAM was not able to do the calculation due to insufficient memory.
The same case was run as a full induction heating simulation, just to illustrate the real time of a simulation. Along with the 8 kHz and 10 kA setup already mentioned we added full thermal calculation for the gear and calculated 4 time steps of heating (2s total heating time) with 3 different meshes (154k, 254k and 344k) on the same 3 machines. As you can see, the total calculation time is more than 3 times larger, and again, at larger mesh (344k) a significant difference in calculation time appears.
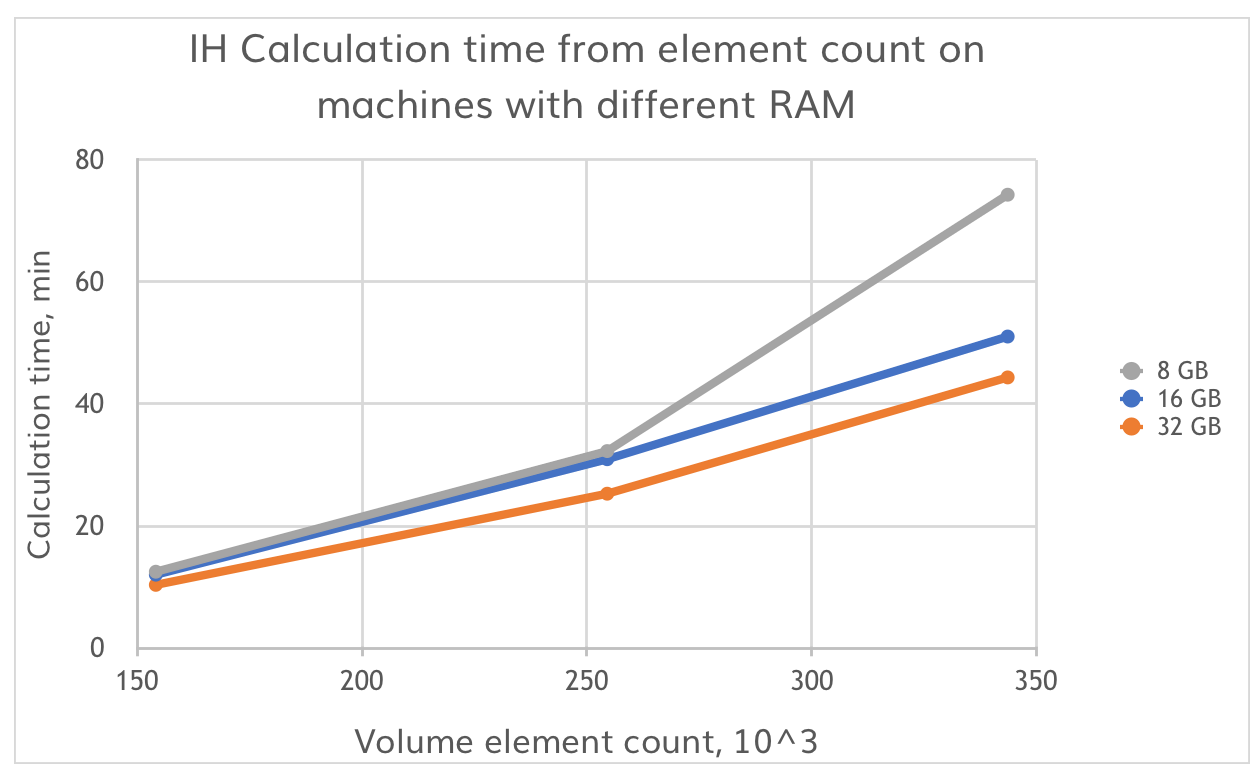
Note: You can download the benchmark case with 344k element mesh and run it on your machine to see where you are in relation with machines we tested and evaluate your hardware.
Conclusion
Hardware is an important aspect that determines the simulation capabilities of your machine. If the RAM size is small, 3D simulations will take more time to calculate, and if RAM size is insufficient, the machine will not be able to run simulations with mesh size larger than a specific element count.
Mesh size directly depends on the complexity of geometry, but if you consider the tips for geometry simplifications found in CENOS Platform documentation page and use the possibility to simulate only part of symmetric geometries, as well as optimize the mesh as much as possible, you can keep the mesh element count even for complex geometries low enough to be able to run your projects with hardware setup as low as 32 GB RAM.
For larger cases bigger RAM size will decrease the calculation time and enable you to run simulations more efficiently, but it is not a necessity to upgrade your machine if you already have at least 16 to 32 GB RAM, as you will still be able to simulate most of the cases.


