Coil loss calculation
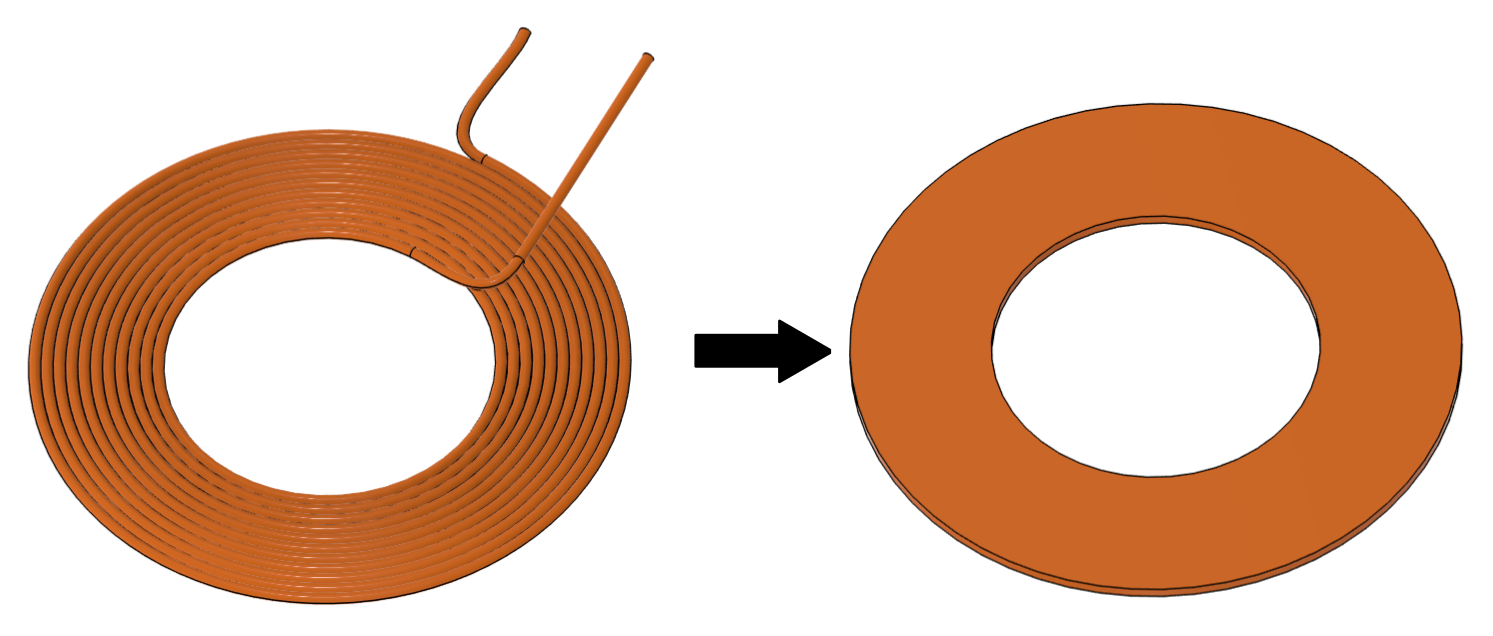
When performing simulations of wireless charging systems, oftentimes we use what seems to be a “drastic” simplification of the physical system to reduce simulation times and make simulations as a viable option for prototyping. One such simplification is used for stranded coils – we don’t need to resolve each winding and strand in our coil CAD files, instead, we can simply replace the coil with a solid block, and use it for the simulation. An obvious question arises – how will this replicate the actual behavior of the coil, and is this approach accurate?
In this article we will take a look how CENOS deals with simplified coil simulations and what approaches are used.
Approach
Setup
Geometrical property definition is divided into 2 parts. First, you define the overall size and placement of the coil with your CAD file, and then in Physics you define the geometrical characteristics of your coils.
Geometry
Load one or multiple coils, simplified to a solid block, into CENOS. This will provide coil width, length, thickness and placement.
Physics
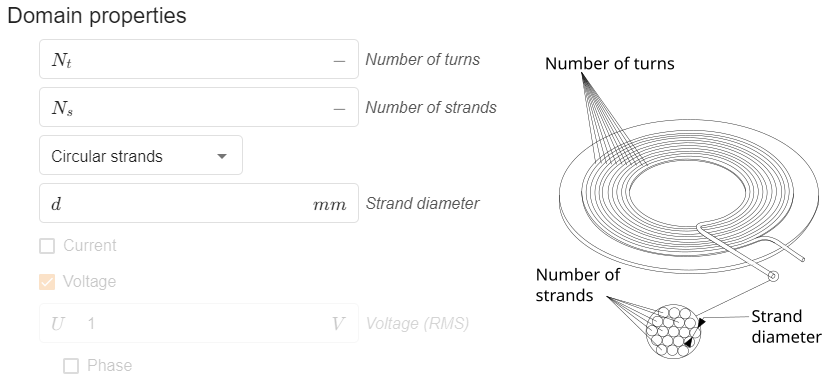
In Physics you need to input more detailed geometrical characteristics for your coils:
- Number of turns
- Number of strands
- Strand size
This will give the remaining information about your coils, so that CENOS could model their behavior correctly.
Results
Loss calculation is represented in the .csv file, which is generated along the visual results. There for every coil along others you can find 2 values – Impedance_re_Ohm and Resistance_Ohm. Intuitively you would expect these values to be the same, but in some cases they appear to be different.
The difference appears because Resistance_Ohm is calculated with analytical equation and represents Ohmic losses of the coil.
Impedance_re_Ohm takes into account Ohmic losses of the coil, as well as resistance from all conductive domains in the system.
If there is no additional conductive parts in the system, the results for Impedance_re_Ohm and Resistance_Ohm will be the same.
References
[1] Muhlethaler, J. (2012). Modeling and multi-objective optimization of inductive power components. Ph. D. Thesis. ETH Zurich. Available at: Diss_Muehlethaler.pdf
[2] C. Carretero, J. Acero, and R. Alonso.: TM-TE decomposition of power losses in multi-stranded litz-wires used in electronic devices, Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 123, 83103, 2012, DOI:10.2528/PIER11091909
[3] Payne A.: The AC resistance of rectangular conductors, 2021. Available at: (PDF) THE AC RESISTANCE OF RECTANGULAR CONDUCTORS

